JS - 반복문(for, while) / 객체활용 for문 / for in / for out 본문
for문
for(정의; 조건; 증감){
출력을 원하는 코드
}
for(let = 0; i<n ; i++){
console.log(i)
}도입이 for로 시작해서 for문
while문
while(i<n){
console.log(i)
i=i+1
}while문 주의 사항 -> 종료 조건을 제대로 설정하지 않으면 무한 반복하게 됨
for문을 활용한 날짜 데이터 리팩토링
어제 만들었던 '남은 시간'을, HTML내에 표현하기 위해 각 변수들을 객체화하였음
remainingObj = {
remainingDays : Math.floor((remainingDate / 3600) / 24),
remainingHours : Math.floor((remainingDate / 3600) % 24),
remainingMins : Math.floor((remainingDate / 60) % 60),
remainingSecs : Math.floor(remainingDate % 60)
}
documentObj = {
days : document.querySelector("#days"),
hours : document.querySelector("#hours"),
mins : document.querySelector("#mins"),
secs : document.querySelector("#secs")
}
이 부분이 특히 중요한데 Object.key(obj)라는 함수를 통해,
각 객체가 가지고 있는 키를 배열화시킴 (for문에서 편히 활용하기 위함)
const remainKeys = Object.keys(remainingObj)
const docuKeys = Object.keys(documentObj)- Dot notation -> obj.property
- Bracket notation -> obj["property"]
객체에서 property를 호출하는 방법에 대해 다시 언급하고 넘어감
console.log(documentObj.days)
console.log(documentObj["days"])
console.log(remainingObj.remainingDays)
console.log(remainingObj["remainingDays"])
완성한 for문
for(let i = 0; i<remainKeys.length; i++){
documentObj[docuKeys[i]].textContent = remainingObj[remainKeys[i]]
}i 가 두 번 삽입된 반복문이라 보기엔 어렵게 보일지언정, 막상 뜯어보면 어렵지 않음 (자기 최면)
documentObj[days].textContent = remainingObj[remainingDays]
documentObj[hours].textContent = remainingObj[remainingHours]
documentObj[mins].textContent = remainingObj[remainingMins]
documentObj[secs].textContent = remainingObj[remainingSecs]위와 같은 코드가 차례로 나열되는 것이라고 볼 수 있음
for in문
for (let key in Obj) {
console.log(key)
}
// 이 때 key는 다른 이름이어도 상관 없음for in문은 위와 같은 형체로 이루어지고, 객체를 대상으로 하는 for문이라는 특징을 가지고 있음
let i = 0;
for(let key in documentObj) {
documentObj[key].textContent = remainingObj[timeKeys[i]]
i++
}타 배열을 불러와 활용하고 싶은 경우, i를 변수로 for문 밖에 지정해 활용해줄 수 있음
for of문
for(let tag of Arr) {
console.log(tag)
}for out문은 위와 같은 형체로 이루어지고, 배열을 대상으로 하는 for문이라는 특징을 가지고 있음
const documentArr = ['days', 'hours', 'min', 'sec']
let i=0;
for (let tag of documentArr){
document.getElementById(tag).textContent = remainingObj[timeKeys[i]]
i++
}
매개변수 (parameter)
함수를 선언할 때 소괄호 안에 정의되는 변수
const sum = function(a,b) {
let result = a + b;
retrun result
}
/ 이때, a,b 는 매개변수전달인자 (arguments)
함수를 호출할 때, 함수 내부로 전달되는 데이터
sum(10, 20) === 30
/ 이때, 10, 20은 전달인자d-day 카운터에서의 활용
const starter = function () {
const targetDateInput = dateFormMaker();
container.style.display = "flex"
messageContainer.style.display = "none"
/// counterMaker(targetDateInput) ///
const intervalId = setInterval(counterMaker, 1000)
intervalIdArr.push(intervalId)
console.log(intervalIdArr)
}/// 부분에서 targetDateInput 을 전달인자로 넣어줌
const counterMaker = function (data) {
console.log(data)
container.style.display = "flex"
const nowDate = new Date();
const targetDate = new Date(data).setHours(0, 0, 0, 0);이때 counterMaker 에서는 해당 전달인자를 data라는 매개변수로 받아 실행함
꼭 data 라고 이름 지을 필요는 없음
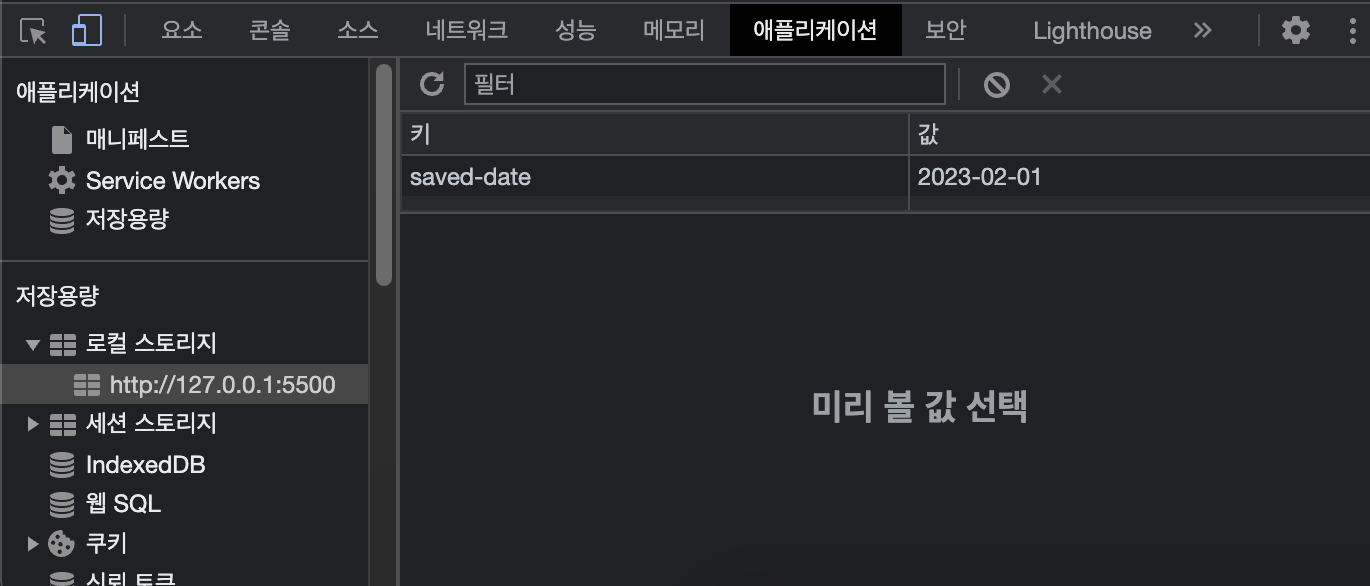
Web storage
Browser에 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 기술
- session storage : 세션 단위로 구분되며 활용(사용자 접속~종료까지) / 브라우저, 탭을 종료 시 영구 삭제
- local storage : 도메인 단위로 구분되며 활용 / key-value 형태 저장 / 브라우저 자체를 종료해도 존재
- 공통점 : key-value 형태 저장 / 로컬 환경에 데이터 저장
// 저장 // localStorage.setItem("saved-date",data)
// 가져옴 // localStorage.getItem("saved-date")
// 삭제 // localStorage.removeItem("saved-date")
localStorage에 저장되어 있는 값
'개발 > JavaScript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JS - todoList (0) | 2022.12.29 |
|---|---|
| JS - 배열 안 객체 활용하기 (1) | 2022.12.29 |
| JS - 함수 / 함수 사용 (1) | 2022.12.27 |
| JS - 데이터, 배열, 객체 (2) | 2022.12.26 |
| JS - setInterval / focus() (0) | 2022.12.21 |



